Manipulator Robotics Introduction
Notes of book Introduction ot Robotics Mechanics and Control.
Notes of book Introduction ot Robotics Mechanics and Control.
There is a lot of development frameworks for Java. This post talks about Guice (for Dependency Injection design pattern implementation), Spring (Java integration environment), JUnit and Mockito (for unit test).
newint, is used to configure the value to 0basethisusingnull: Means a reference type points to nothingNullable<T> T?IsNullINullable interface??(A ?? B): return the non-null object. Check A firstlyExplicitpublic static explicit operator XX(para)Implicitpublic static implicit operator XX(para)#if, #else, #elif, #endif[Conditional("Debug")]#define, #undef#define Debug for the conditional compile#warning, #error#region, #endregion#pragmachecked, uncheckedyieldyield return is used to return a value in the enumerator. The return type of the method belongs to System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator<T>, System.Collections.IEnumerable or etc.yield break is used to end the enumerating.locklock(xx) to add a lock for the xx object, so that if other threads want to call this object, they need to wait current thread to finish the process on this object.unsafe*, &, sizeof to avoid the CLR and operate the memorysealedoverride keyword togetherTypeName: type nameProperty Name: type name containing the namespaceAssemblyQualifiedName: type name containing the namespace and assemblyconst or readonly values are assigned a value, the value couldn’t be changed. constnew keywordreadonly or static readonlyClassStructnew to instantiate
Actually they have no relationship to each other.
Attribute
System.Attribute[], support multi attribute[AttributeUsage()]: Control how to apply customized attributes to targeted element[Flags]: Regard the value of enum as bit flag rather than value[DllImport()]: Call the un-managed code. e.g. Win32 API method[Serializable]: Indicate the element could be serialized[Conditional()]: Support the conditional compileProperty
See here for more info.
Class can implement interfaces and inherit another class.
Interface doesn’t inherit from System.Object. Methods in an interface are abstract methods, so interface cannot be instantiated but only be implemented by other classes. Classes implement one interface need to implement all the abstract methods or properties in the interface. It supports the polymorphisn.
For abstract class, it also contains the abstract methods and the abstract class cannot be instantiated but only be inherited. Classes which inherits a abstract class need to implement all the abstract methods. Apart from the abstract methods, the abstract class can also include some public and virtual methods which contains the body. So the subclass can use those methods directly. It supports the polymorphisn.
Some use cases are as follow.
| Interface | Abstract Class |
|---|---|
| Provide common method for unrelated classes | Provide common elements for related classes |
| Defines the action | Defines the properties, pre-defined methods, common fields |
| Usually not change after create | Can be used in multi-version scenarios |
Subclass converting to base class can be achieved implicitly, while base class converting to subclass needs to be achieved explicitly.
is: Is used to determine whether this type can be converted to another type. Return false is object is null.as: Convert the type. Return null if object is null.| override | overload |
|---|---|
| For subclass to override the virtual/abstract method in base class | In one class, contains several methods with the same name |
| method name and parameters and return type should be same | methods with the same name but with different parameters list |
| Dynamic binding. Method calling is confirmed in CLR. CLR will check the proper method for a base class reference according to type of its instance | Static binding. Method calling is confirmed in the compile |
| For override the generic method, the constrains of generic method in base class will be inherited. | Generic method could also serve as the overload method |
Use = for value type is deep copy; Use = for reference type is mainly shallow copy. (String is deep copy)
Inherit interface ICloneable to customize the Object Clone() method. e.g. return a new object
Use static field to define a Singleton class.
| Static | Non-static | |
|---|---|---|
| Class | Only contains static field and static method Cannot be instantiated |
Can contains static method and non-static method Can be instantiated |
| Method | Can only use static field and static method | Can use any field and method |
Dynamic is the keyword and a class. It can be used for field, property, method, indexer, parameters, return value, local variable. The specific type of the element declared dynamic will be determined during the CLR/DLR.
| var | dynamic | System.object |
|---|---|---|
| type will be determined during compile | type will be determined in CLR/DLR | a instance type |
| only ca be used for local variable | can be used for everything | can be used for everything |
Dynamic solve the dynamic bind for objects. It combines C# with other dynamic language like IronPython, IronRuby.
1 | ScriptRuntime py = Python.CreateRuntime(); |
Dynamic can also dynamically add a filed or property to a class.
Object is the top base class for any other classes in .NET C#. The base methods of System.Object contains:
GetMembers and GetMethods to get the instance of this typepublic virtual bool Equals(object obj)GetHashCode the same timepublic static bool Equals(object objA, object objB)public static bool ReferenceEquals(object objA, object objB): compare whether 2 objects are points to the same instance==Note: String is a very special type.
There are two kinds of constructors. Their IL forms are as follow.
.ctor: object constructor.cctor: type constructor (static constructor).NET also provide a flexible constructor to allow to set the properties in the constructors.
1 | User user = new User {Name = "aa", Age = "bb"}; |
String is a sealed class. It is a reference type but shows value type features when using.
Immutability. Once a string is created in the memory, it cannot change. Any actions including Insert, Substring, ToUpper will create a new string.
String interning. When the CLR loads, it will create a resident pool. This pool won’t be controlled by GC or Every unique string value in code will store in this resident pool. CLR will also create a hash map, the key is the string stored in resident pool and the value is the address. When creating a string value by assigning a unique value, it will store that value in resident pool and assign the address to this string. When assigning a value appeared before, CLR will assign the address checking from hash map to this string.
Note. If a string is assigned dynamically e.g. assigned by other string, the result value of this string won’t be stored in the resident pool. Use System.Intern(xx) can add it to resident pool.
For convert. Some value types already override the ToString method for converting itself to a string. To convert a string to other value types. e.g. Double.Parse(str), Double.TryParse(str, out num), num = Convert.ToDouble(str)
StringBuilder can help to append several strings and convert to a string together.
System.Enum inherits from System.ValueType. Default, the first element equals to int 0. The value of the element can also equals to bit number 0x00 if the attribute [Flags] is added to the enum. At this time, a enum variable supports the | operation.

Common methods contain
GetNames(typeof(X)): Get all names of the enumGetValues(typeof(X)): Get all value of the enumIsDefined(typeof(), XX): Check whether the name of value in the enumCollection is a container to control a bunch of objects. The collection can be treated as a whole object and every object can also be get separately.
Collection is a class in .NET. The common methods for most collections types include:
| Method | Function |
|---|---|
| Add | add new item |
| Insert | insert new item in a specific index |
| Remove | remove a particular item |
| Clear | remove all items |
| IndexOf/LastIndexOf | find the index of a particular item |
| Sort | sort items |
| GetEnumerator | return value when iterated calling |
| Count | the count of all items |
| Item | get a specific item |
For a collection, it should implement the IEnumerator interface, which support MoveNext and Reset methods, and Current property. Then in C#, users can use foreach to get the value from the enumerator.
For a collection, it should implement the Synchronized method, which support for the safe action on the object in the multi-thread code.
The category of collections include:
ICollectionStackStack<T>QueueQueue<T>IListArrayArrayListList<T>IDictionaryHashtableDictionary<TKey, TValue>SortedDictionarySortedListSortedList<T>For customized collection, users can inherit the CollectionBase abstract class or implement interfaces like ICollection, IList.
Delegate is a class which implements a safe type callback method. Delegate is like the method pointer in C++. It defines the return type and parameters list. A delegate type needs to be instantiated and then added other methods. By calling this delegate directly or use its Invoke method, it could callback other methods added to this delegate.
For multi-methods added to the delegate, it is called multicast. Methods could use += or -= to bind or unbind to the delegate. The order of callback those methods is the same with the order to bind to the delegate.
There is some pre-defined delegate in C#, which include
Event model is also based on delegate. It is a encapsulation for delegate. See here for more examples about delegate and event.
Anonymous method is a method without name but have the expression body.
Delegate keyword can be used to declare an anonymous method. The anonymous method can be assigned to a delegate variable.
1 | delegate void MyDelegateType(int x, int y); |
Lambda Expression can also be used to declare an anonymous method. The form is Argument => expression or (Arguments) => {expression}. Compared with using delegate to declare anonymous method, it don’t required to declare the type of the arguments because the compiler will set the type automatically.
1 | MyDelegateType myDelegateInstance = |
1 | public class test<T> {} |
T isn’t assigned a specific type T is value type, JIT will generate different naive code by replace the T with different value typesT is reference type, there will only be one copy of naive codeSystem.Collections.GenericList<T>SortedList<TKey, TValue>Queue<T>Stack<T>Collection<T>Dictionary<TKey, TValue>When instantiate a parameterized type field, the default keyword can be used, which will return 0 for value type and null for reference type.
1 | public class test<T> |
The generic can use where keyword to add constraints for the parameterized type.
1 | public class test<T> where T: constraint1, constraint2, ... |
| Constraint | Function |
|---|---|
| T: struct | The type T must be value type |
| T: class | The type T must be reference type |
| T: class name | The type T must be the named class or its derived class |
| T: interface | The type T must contains or implement those interfaces. The interfaces could also be generic interfaces |
| T: new() | The type T must contain a constructor without parameters |
Generic method can exist in a generic class or a non-generic class.
1 | class MyClass{ |
Interface can also have generic features. Some generic collections class implements those generic interfaces. e.g. IList<T>, IComparable<T>
1 | class MyArray<T>: IComparable<T> {} |
Delegate can also have generic features. e.g. delegate string MyMethod<T>(T t).
Generic delegate can also use for event. Like EventHandler<TEventArgs>. It is defined as delegate void EventHandler<TEventArgs>(object sender, TEventArgs e)
1 | using System; |
EventHandler<TEventArgs> for event definitionNullable<T> for handling null conditionIEnumerable<T> for achieving enumeratorSystem.Object or System.Type
trycatch or finallycatchSystem.ExceptionDivideByZeroExceptionStackOverflowExceptionFileNotFoundExceptionthrow to throw the exceptionfinallySystem.Exception is a class, which contains
Safety models structure of .NET
IPrincipalIsInRole and IdentityGenericPrincipal for generic users and WindowsPrincipal for Windows users.IIdentityAuthenticationType, IsAuthenticated, and NameGenericIdentity, WindowsIdentity, FormsIdentity for ASP.NET application and PassportIdentity which requires Passport SDK.PrincipalPermissionAttribute or PrincipalPermission class to declarative or explicitly check the accessFileIOPermissionEnvironmentPermissionEventLogPermissionDemand, LinkDeman, Assert to declarative or explicitly check the access.NET Framework includes CLR (Memory Management, Thread Management and Remote Process) and FCL, which is a object-oriented collection of reusable types. FCL needs to provide API for program and it provides a tree type structure. FCL assemblies is stored as .dll files in disks.
The node of the FCL structure is called namespace, which contains class, struct, enum, delegate, interface. The namespace is only the logic structure of the FCL structure rather than the physical structure of the assembly. The same namespace could stored in different assemblies. Common namespace are as follows.
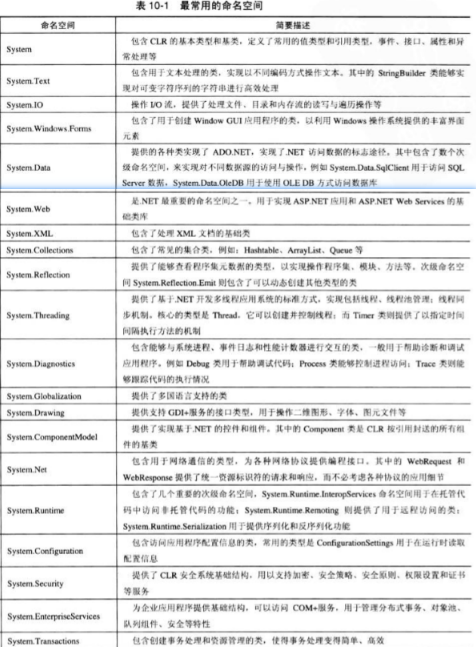
System namespace contains many basic data type. It includes
ObjectValueTypeInt16, Int32, Char, Boolean, DoubleStringArrayDelegateAttributeTypeNullableIt also includes many basic services
It contains handle for the file, folder and memory stream.
It is related to the serialization (convert object to a saveable or transmittable format) and deserialization (recover the object from physical material or stream).
BinaryFormatterSoapFormatterXmlSerializerHandle the system process, event log and help to debug.
Metadata and IL Language are the fundamentals of CLR. Metadata describes the static structure and IL Language
describes the dynamic execution.
Metadata is fundamental data that is used to describe other complex data.
For the .NET metadata, it is used to describe: class, type, property, method, filed, parameters, attribute. The main category of .NET metadata are:
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| Definition Form | TypeDef, MethodDef, FieldDef, ModuleDef, PropertyDef |
| Reference Form | AssemblyRef, TypeRef, ModuleRef, MethodsRef |
| Pointer Form | MethodPtr, FieldPtr, ParamPtr |
| Heap | #String, #Blob, #US, #GUIDe |
Below is the metadata to describe the Main function of class Program
; |
Person person: Reference typeinitobj0, and reference type of class to nullnew Person(): Value typenewobjctor constructor methodInitialization of some special type
newobjIL has two keywords to describe the method type.
static keyword to declarecall keyword to executeinstance keyword to declarecallvirt to executecall: call the method according to the static type of the reference, mainly used for non-virtual method.Equals, ToStringcallvirt: call the method according to the dynamic type (real object) of the reference, mainly used for virtual method.calli: call the method through a method pointerIdftn or Idvirtftn command get the method pointerMethodInfo.Invoke() and Dynamic Method DelegateSystem.Object.ctor method: class constructor method.cctor method: class type constructor method.cs to .exe.dll or .exe.cs to .il.il and .exe.il to .exe.exe to .ilctrl + m could view the metadata in that code.CTS defines the types and rules for different programming language based on .NET. It defines the relationship between each language with their IL program.
Like in C#, the type of int, char, string corresponds to System.Int32, System.Char, System.String.
The type in the content of CTS includes the following chart.
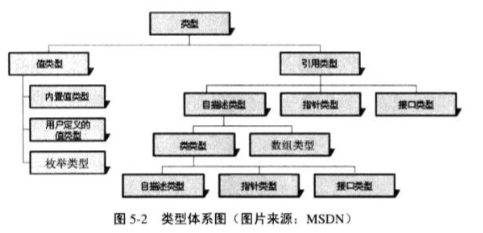
SystemPrimitive type in C# and FCL
| C# | FCL |
|---|---|
| int | System.Int32 |
| long | System.Int64 |
| floaat | System.Single |
| string | System.String |
| object | System.Object |
int, char, long, bool, float, double, byte, enum, struct.System.ValueType (which inherits from System.Object)Equals method, could compare the value of two data instead of the addresses of two dataclass, interface, delegate, object, string and int[] etc.System.ObjectString is very special. The equals of string will compare the value instead of the address. Every action on the string will generate a new string data in the managed heap.ref, out)static public implicit operator XX(YY y) to write a method can customize the convert between different typeFor the convert between value type and reference type, we need to use boxing (from value to reference) and unboxing (from reference to value) to achieve it.
Note. unboxing must happen in the reference type which is generated from boxing process.
The boxing and unboxing will influence the efficiency. Use generic could avoid influencing the efficiency.
Examples of boxing and unboxing
| Value Type | Reference Type | |
|---|---|---|
| Value Passing | Inner change won’t influence outside | Inner assign action influences outside, but the initialization won’t influence outside |
| Reference Passing | Any change will influence outside | Any change will influence outside |
For reference passing, must use ref or out
ref: must be initialized before passingout: must be initialized inside method.NET CLR has 3 part of memory.
When call an instance method. The next command will be pushed to stack of thread, then other local value type will be pushed to the stack. When finish, those value type will be pop until get the pointer to the next command.
GC Heap stores the instance of reference type. Manged by GC. The instance will contains a TypeHandler which points to its method table in the Loader Heap.
Loader Heap stores the metadata (type). Every type in the loader heap is a method table. Managed by AppDomain. The method table has a part called Method Slot Table, which is a linked list containing the methods. When call a method in a reference type (class), CLR will follow the TypeHandler in the GC heap to find the metadata which contains this type’s definition in Loader Heap. Then CLR will check the Method Slot Table in this method table, and use JIT to compile the method’s IL code to naive code. The naive code will be stored in a dynamic memory.
 in Pythonse.add(item) se.remove(item)The time complexity of search in HashTable’s key or HashSet is O(1)
collections.Counter(list) can count the element in the list and generate a dictionaryfor key, value in dic.items() can iterate the key and value at the same timesorted(dic.keys()) is sorting the keysdic.get(key, value) return the dic[key] if the key in dic, otherwise return value you giveNo.1 Two Sum
1 | dic = {} |
No.138 Copy List with Random Pointer
No.202 Happy Number
No.136 Single Number
1 | se = set() |
No.217 Contains Duplicate
No.3 Longest Substring Without Repearting Characters
No.49 Group Anagrams
1 | dic = {} |
No.347 Top K Frequent Elements
Swap the key and values
1 | form = dict(collections.Counter(nums)) |
No.387 First Unique Character in a String
No.242 Valid Anagram
No.350 Intersection of Two Arrays II
No.36 Valid Sudoku
No.454 4Sum II
Queue and stack are just like a store. You just want to put and pick the items one by one. The time complexity of put and pick is O(1)
Python makes queue and stack easier because we can use list to finish the functions of queue and stack.
1 | my_queue = [] |
No.94 - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
No.103 - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
No.20 - Valid Parentheses
No.42 - Trapping Rain Water
To be continued…
Fenwick tree is also called Binary Indexed Tree. This kind of data structure can do the calculation of sum from 0 to ith of a list very efficiently.
It can also be used to calculate the frequency. Below is a code used to calculate the number of values from 0 to i.
1 | class fenwickTree: |
Relevant application is in Leetcode No.315.
Heap is a useful data structure which can store the elements in order. In Python, there is a built in heap library called Heapq.
No.253 - Meeting Room
There are 7 main sorting algorithm, which are also connected with other conceptions. Will be finished in the future.
$O(n^2)$
$O(nlog(n))$
$O(n^2)$
$O(nlog(n))$
$O(n^2)$
$O(nlog(n))$
$O(nlog(n))$